British Airways flight BA2156 was operating a scheduled service from VC Bird International Airport, Antigua (ANU), West Indies to Robert L Bradshaw International Airport, St Kitts (SKB), West Indies and return.
The sector from ANU to SKB was uneventful.
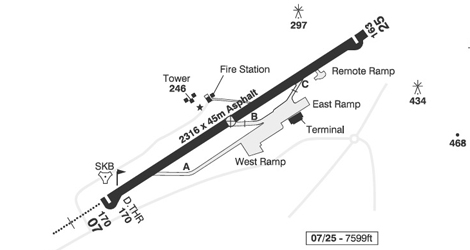
On arrival at SKB the aircraft was not parked on a designated stand but at an angle of approximately 45° to the terminal. This allowed the aircraft to self-manoeuvre off the stand as no pushback tug was available.
This was the first time the commander or the co-pilot had operated to or from SKB.
British Airways flight BA2156
Flight planning for the return sector was completed by the commander and the co-pilot on the flight deck. Takeoff performance data for both the full length and from Intersection Alpha on Runway 07 were requested via the on‑board data communications system. Once the speed and thrust setting were calculated, the crew agreed that the takeoff performance was satisfactory from Intersection Alpha and that this was considered preferable to backtracking the runway for a full length departure. The co-pilot was the handling pilot for this sector and although, prior to engine start, he briefed the departure from SKB and the arrival at ANU, he did not brief the taxi routing. He considered that the aerodrome charts provided lacked clarity and information. At the time of the incident it was daylight but the sun was low to the west. A member of the cabin crew was also on the flight deck, sitting on the jump seat.
Once the co-pilot had lined up the aircraft and stopped, the commander stated that the runway looked very short. He advised the co-pilot to “stand on the brakes” and apply 55% N1 before brake release, which the co-pilot did.
Both pilots felt that the aircraft accelerated quickly to 80 kt. The co-pilot then considered the acceleration to V1 to be much slower and noticed that the end of the runway was approaching. V1 was achieved as the aircraft reached the touchdown zone aiming point markers for Runway 25 and rotation was commenced with the aircraft lifting off shortly afterwards. Intersection Bravo on Runway 07 is not authorised, for Boeing 777 takeoffs, by this aircraft’s operator.
British Airways flight BA2156 had taken off with a Takeoff Run Available (TORA) of 1,220 meters ; the performance calculations were based on a TORA of 1,915 meters.
Contributory factors to British Airways flight BA2156 serious incident were :
- The airport authority had not installed any taxiway or holding point signs on the airfield.
- The crew did not brief the taxi routing.
- The crew misidentified Taxiway Bravo for Taxiway Alpha and departed from Intersection Bravo.
- The trainee ATCO did not inform the flight crew that they were at Intersection Bravo.
Download Report


0 Comments