On 3 July 2014 at 1815 hours (local time), a Singapore Airlines flight SQ61 aircraft departed Houston in Texas, USA via the INDIE ONE Standard Instrument Departure (SID).
The INDIE ONE required the aircraft to maintain 4,000ft or other altitudes as assigned by ATC. However, after departure the B777 climbed above 4,000ft, thus conflicting with another aircraft which was descending to 6,000ft. An air traffic controller noticed the potential conflict and instructed the B777 to descend to 5,000ft.
It was estimated that, at their closest, the aircraft were 0.61NM and 200ft apart.
The US National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) did not formally investigate into the occurrence, which was regarded as a pilot deviation from an ATC clearance, but reviewed the circumstances with the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) and provided information relating to this occurrence to the AAIB, including an initial report on the occurrence by FAA.
SINGAPORE AIRLINES flight SQ61
However, the AAIB regarded the occurrence as being significant enough to merit a report to highlight the safety lessons. The factual information in the report is largely based on the inputs of the NTSB, FAA and the operator.
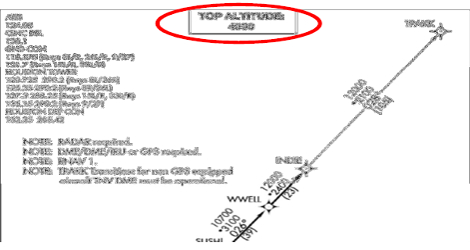
The TCAS TA/RAs were the result of the flight crew not noticing the altitude restriction of 4,000ft in the Jeppesen chart for the INDIE ONE RNAV SID.
On the one hand, the pilots were not being systematic in the way they conducted the departure briefing and read the Jeppesen chart.
After reading the first line in the ‘Routing’ section of the text box at the bottom left corner of the chart, the PF of Singapore Airlines flight SQ61 scrolled to the pictorial portion at the right of the chart and zoomed in to check on the track and distances. He ended his briefing on the chart without returning to the ‘Routing’ section of the chart, which contained an altitude restriction of 4,000ft. This omission was not picked up by the PM and C2. This suggests ineffectiveness of the monitoring action on the part of the PM and that there is room for improvement in crew resource management (CRM) training.
On the other hand, had the altitude restriction of 4,000ft appeared more prominently in the Jeppesen chart, the flight crew might have been able to notice such a piece of information.
Singapore Airlines flight SQ61 : as it was, the SID’s altitude restriction was not found in the ‘Initial Climb’ section, but was in SID’s text box under the ‘Routing’ section.
It is not intuitive to look for information on altitude restriction for the Initial Climb phase in the ‘Routing’ section.
Download Report


0 Comments