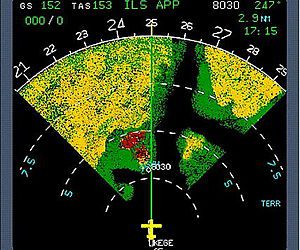
Eastern Airlines flight EAL410 operated with a Lockheed 1-1011 crashed at 23:42 eastern standard time, December 29, 1972, 10.7 miles west-northwest of Miami International Airport, Miami, Florida. The aircraft was destroyed. Of the 163 passengers and 13 cremembers aboard, 94 passengers and 5 crewmembers received fatal injuries. Two survivors died later as a result of their injuries.
Following a missed approach because of a suspected nose gear malfunction, the aircraft climbed to 2, 000 feet mean sea level and proceeded on a westerly heading. The three flight crew members and a jumpseat occupant became engrossed in the malfunction.
The National Transportation Safely Board determines that the probable cause of this accident was the failure of the flightcrew to monitor the flight instruments during the final 4 minutes of flight, and to detect an unexpected descent soon enough to prevent impact with the ground.
Preoccupation with a malfunction of the nose landing gear position indicating system distracted the crew’s attention from the instruments and allowed the descent to go unnoticed.
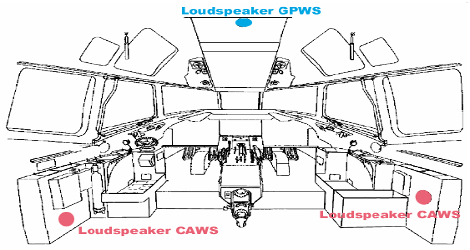
GPWS, or Ground Proximity Warning System, acts as a guardian angel for pilots during critical landing phases. Here’s how it works in under 300 words:
The Last Line of Defense: Imagine an aircraft unknowingly getting dangerously close to terrain, obstacles, or even the ground during landing. GPWS is a computerized voice alert system that warns pilots of such impending threats, providing a crucial buffer zone to prevent Controlled Flight Into Terrain (CFIT) accidents.
Seeing the Unseen: Relying solely on visual cues can be risky, especially in low visibility conditions. GPWS utilizes various inputs like altitude, radio altitude (height above ground), and descent rate to create a real-time picture of the aircraft’s proximity to danger zones.
Vocal Warnings: As the aircraft gets closer to terrain, obstacles, or descends too quickly, the GPWS kicks in with a series of increasingly urgent voice callouts. These clear and concise audio warnings like “Pull Up!” or “Sink Rate!” leave no room for misinterpretation and prompt pilots to take corrective action.
Customizable Zones: The GPWS isn’t a one-size-fits-all system. It can be programmed with different warning thresholds depending on the landing phase and terrain profile. This ensures timely alerts without bombarding pilots with unnecessary warnings during normal descents.
Beyond Landings: While crucial for landings, GPWS can also be helpful during other flight phases, like go-arounds (abandoned landings) or during low-altitude flying maneuvers.
A Teamwork Approach: GPWS is a valuable tool, but it’s not a substitute for pilot vigilance and sound decision-making. It functions best when pilots use it in conjunction with other instruments and visual cues to maintain situational awareness and ensure a safe landing.
Precision Air – ATR42-500 (5H-PWF) flight PW494
Precision Air flight PW494 was operated with an ATR42-500 (registration 5H-PWF) from Julius Nyerere International Airport, Dar es Salaam for a scheduled commercial passenger flight to Bukoba on 06-11-2022. Weather at destination Bukoba airport was poor and last part...
GPWS vs EGPWS
GPWS vs EGPWS Ground Proximity Warning System (GPWS) and Enhaced Proximity Warning System (EGPWS) are safety systems that are installed on aircraft to provide pilots with visual and auditory warnings of potential ground collisions. GPWS utilizes a combination of...
Sirwijaya Air – Boeing B737-500 (PK-CLC) flight SJ182
On 9 January 2021, Sirwijaya Air flight SJ182 took off from Soekarno-Hatta International Airport (WIII), Jakarta with intended destination of Supadio International Airport (WIOO), Pontianak, and operated with a Boeing B737-500 registration PK-CLC. At 0736 UTC (1436...
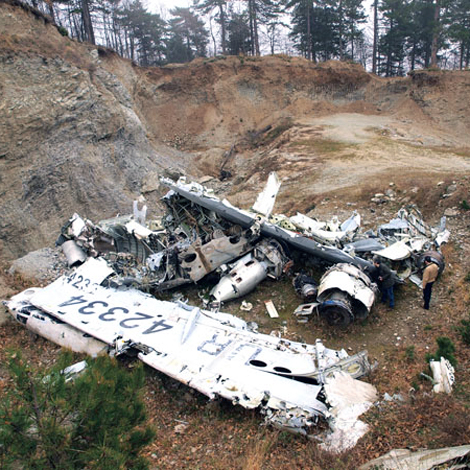
Aerosweet Airlines – Yakovlev YAK42 (UR-42334) flight AEW241
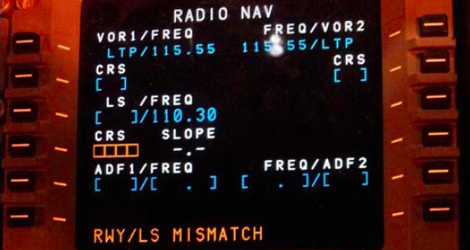
Aerosweet Airlines flight AEW241 was a regular scheduled passenger flight from Odessa International Airport, Ukraine, to "Makedonia" International Airport Thessaloniki Hellas. The flight was approaching by VOR/ILS procedure, for landing on runway 16. Executing the...
American Airlines – Boeing B757-223 (N-651AA) flight AA956
American Airlines flight AA956 , also known as the Calì accident , was a regularly scheduled passenger flight operated with a Boeing 757-223, N651AA, from Miami International Airport (MIA), Florida, U.S.A., to Alfonso Bonilla Aragon International Airport (SKCL), in...
Aeroperu Boeing B757-200 (N52AW) flight PL603
Aeroperu flight PL603 was operated by Aeroperu with a Boeing B757-200 (N52AW and took off at 05:42 UTC on 2 October 1996 from Jorge Chávez International Airport in Lima, Peru bound to Santiago de Chile. When Aeroperu flight PL603 took off and reached speed V2 + 10,...
Adam Air – Boeing B737-300 (PK-KKV) flight KI172
On 21 February 2007 at 1525 local time (0825 UTC), Adam Air flight KI172 , registered PK-KKV, was being operated by PT. Adam Sky Connection Airlines (Adam Air) on a scheduled passenger flight from Soekarno-Hatta Airport, Jakarta to Juanda Airport, Surabaya, East...
Sirwijaya Air – Boeing B737-300 (PK-CKM) flight SJ230
Sirwijaya Air flight SJ230 , a Boeing 737-300 registered PK-CKM, was being operated by PT. Sriwijaya Air on On 20 December 2011 from Soekarno Hatta International Airport (WIII) Jakarta to Adisutjipto International Airport (WARJ), Yogyakarta. There were 141 persons on...
Kelowna Flightcraft Air Charter – McDonnel Douglas DC3C (C-GWUG) flight KFA300
The accident aircraft, Kelowna Flightcraft Air Charter flight KFA300 was under charter to Purolator Courier Ltd. (Purolator). Since April 1998, the aircraft had been dedicated to transporting cargo on a route between Vancouver and Nanaimo, British Columbia. On...
Loganair – SAAB 2000 (G-LGNO) flight LM0080
The Loganair flight LM0080 was serviceable with no relevant deferred defects prior to the fight. Weather forecasts for Sumburgh predicted thunderstorms with rain, snow, and hail, and winds gusting up to 60 kt, during the afternoon and early evening. The aircraft and...
ACT Airlines – Boeing B747-412F (TC-MCL) flight TK6491
On January 1st 2017 the crew of a cargo Boeing 747-412F a/c registration TC-MCL operated by ACT Airlines including Captain, FO, loadmaster and a/c...
Itek Air – Boeing B737-200 (EX-009) flight IRC6895
Itek Air flight IRC6895 was a flight from Bishkek to Teheran, flown on 24 August, 2008 with a Boeing 737-200 aircraft registered ЕХ-009 . Souls onboard where the PIC plus co-pilot, cabin crew (3 persons) as well as 85 passengers including two service passengers: a...
Garuda Indonesia – Boeing B737-497 (PK-GZC) flight GA200
On 7 March 2007, Garuda Indonesia flight GA200, a Boeing B737-497 registered PK-GZC , was being operated by Garuda Indonesia on an instrument flight rules (IFR), scheduled passenger service, from Soekarno-Hatta Airport, Jakarta to Adi Sucipto Airport, Yogyakarta....
Aom Minerve S.A – McDonnell Douglas MD-83 (F-GRMC) flight IW68
The evolution of the Aom Minerve flight IW68 was analyzed on the basis of flight documents, recorded data and witness statements. On Sunday 23 November 1997, the crew flew the Toulon-Orly-Marseille route stages : on the previous day, they had flown the...
Air Blue – Airbus A321-231-A5 (AP-BJB) flight ABQ202
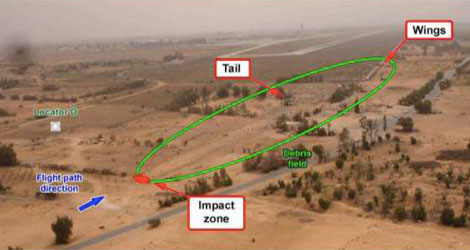
Air Blue flight ABQ202 , operated with an Airbus A321 (AP-BJP) on 28 July 2010, was a scheduled domestic flight sector Karachi - Islamabad. The aircraft had 152 persons on board, including six crew members. Air Blue flight ABQ202 took-off from Karachi at 0241 UTC...
Qantas – Boeing B737-400 (VH-TJX)
On 18 January 2001, Qantas flight VH-TJX, a Boeing 737-476 aircraft, encountered microburst windshear at 0729 EST while conducting a go-around from runway 19 at Brisbane aerodrome during an intense thunderstorm. The aircraft was operating a scheduled fare-paying...
Jet Airways – Boeing B737-800W (VT-JFA) flight IX374
Jet Airways flight IX374 was operated on 17/08/2015 with a Boeing B737-800 aircraft registration VT-JFA. The flight was a Doha-Cochin sector . Both the operating crew were duly qualified on type B737 aircraft to operate the flight. There were 142 passengers and 08...
Sukhoi-Alenia – Superjet 100 (RRJ–95B) flight RA36801
Sukhoi-Alenia - Superjet 100 (RRJ-95B) flight RA36801 , registered 97004, on 9 May 2012 was conducting a demonstration flight from Halim Perdanakusuma International Airport, Jakarta. The accident flight was the second of two scheduled demonstration flights. On board...
Air India Express Boeing B737-800 (VT-AXV) flight IX812
Air India Express flight IX812 was a scheduled Quick Turn Around (QTA) daily flight , on sector Mangalore-Dubai-Mangalore. On 21st / 22nd May 2010, a similar flight was operated by the same cockpit crew , along with 4 Cabin crew. As per the schedule, the crew had been...
Air Nippon – Boeing B737-800 (JA-55AN) flight ANA325
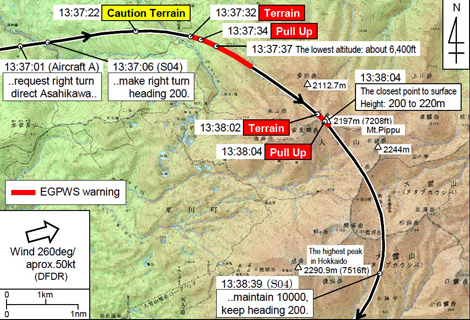
The occurrence of Air Nippon flight ANA325 covered by this report falls under the category of “A case where aircraft crew executed an emergency maneuver during navigation in order to avoid a contact with the ground” as stipulated in Clause 5, Article 166-4 of the...
Mandala Airlines – Boeing – B737-200 (PK-RIL) flight MDL260
On 1 November 2007, a Boeing Company B737-200 aircraft, registered PK-RIL, operated by Mandala Airlines flight MDL260 , was on a scheduled passenger flight from Jakarta Soekarno-Hatta International Airport, Jakarta, to Abdurrachman Saleh Airport, Malang, East Java....
Kenya Airways – Boeing – B737-800 (5Y-KYA) flight KQA507
During the night of 04th May 2007, the B737-800, registration 5Y-KYA, operating as Kenya Airways flight KQA507 from Abidjan international airport (Cote d'Ivoire), to the Jorno Kenyatta airport Nairobi (Kenya), made a scheduled stop-over at the Douala international...
Kingfisher Airlines – ATR – ATR72-212 (VT-KAC) flight IT4124
Kingfisher Airlines flight IT4124 , an ATR-72-212 aircraft VT-KAC was schedule to operate flight IT4123 Mumbai-Bhavnagar and IT-4124 (Bhavnagar –Mumbai) on 10.11.2010. Prior to operating the flight IT-4123 both the crew underwent the pre-flight medical examination and...
Ryanair – Boeing – B737-800 (EI-CSA) flight FR058
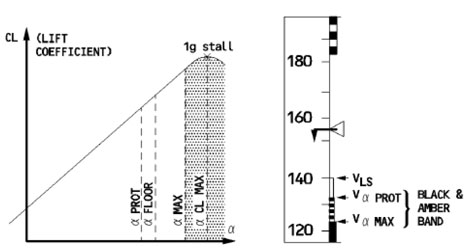
Ryanair flight FR058 departed London Stansted , the aircraft climbed to its allotted cruising level, with the Captain as the Pilot Flying (PF) and the First Officer as the Pilot Not Flying (PNF). This was the PF’s last day of duty for the Operator. He would be...
Germanwings – Airbus A320-211 (D-AIPX) – flight 4U9525
On Tuesday 24 March 2015, the Airbus A320-211 registered D-AIPX operated by Germanwings was programmed to undertake scheduled flight 4U9525 between Barcelona (Spain) and Düsseldorf (Germany), with the callsign ‘‘GWI18G’’. Six crew members (2 flight crew and 4 cabin...
Naske Air – Dassault Falcon – Falcon 20 (D-CBNA)
Naske Air Falcon 20 D-CBNA was part of a non-scheduled international cargo flight from Gdansk (EPGD) to Louisville (KSDF). The flight crew had previously on August 4, 2001, on another charter flight, flown the aircraft from Hanover (EDDV) to Palma de Mallorca (LEPA)...
Air France – Airbus – A319-111 (F-GRHU) flight AF2184
Air France flight AF2184 was operated with an Airbus A319 between Paris Charles de Gaulle and Tunis Carthage. The briefing was carried out at 5 h 00, takeoff took place at 6 h 53 min. The Captain was Pilot Flying (PF). In cruise at FL 350, the PF prepared an arrival...
Hermes Airlines – Airbus – A320 (SX-BHV) flight BIE9861
The crew took off from Ajaccio bound for Lyons Saint-Exupéry. The flight was chartered by Air Méditerranée and performed by Hermes Airlines. The Captain was the instructor (PNF) and was sitting in the right-hand-side seat. The student /pilot in-command was PF in the...
Enerjet – Boeing – B737-700 (C-GDEJ) flight ENJ401
Enerjet flight ENJ401 was operated with a Boeing B737-700 (registration C-GDEJ, serial number 32427) from Fort St. John to Fort Nelson, British Columbia. At 1117 Mountain Standard Time, during the landing rollout on Runway 03, Enerjet flight ENJ401 overran the runway...
Bradley Air Services LTD (First Air) – Boeing – B737-210C (C-GNWN) flight FAB6560
Bradley First Air flight FAB6560 , Boeing 737-210C combi 2 aircraft departed Yellowknife (CYZF), Northwest Territories, at 1440 as First Air flight 6560 (FAB6560) on a charter flight to Resolute Bay (CYRB), Nunavut, with 11 passengers, 4 crew members, and freight on...
Sichuan Airlines – Airbus – A319 (B-6054) flight 3U8949
Sichuan Airlines flight 3U8949 was an Airbus A319 (B-6054) . The plane took off from Chongqing airport at 07:45. At 08:47, the flight crew confirmed that the special report about the thunderstorms at Destination airport (see Appendix I) sent by CSC Dispatching Office...
Afriqiyah – Airbus A330-202 (5A-ONG) flight 8U881
Afriqiyah A330-202 registration 5A-ONG was on schedule flight from O.R Tambo International Airport - Johannesburg (South Africa) to Tripoli international Airport (Libya).The Aircraft took off on May 11th 2010 at 19:25 UTC flight number (8U 771). There were three...
Europe Airpost – Boeing – B737-300 (F-GFUF) flight FPO227
Europe Airpost flight FPO227 : the history of the flight is based on testimony from the pilots and analysis of the FDR parameters. The absence of the CVR recording (communications and aural warnings in the flight deck, in particular) and data from ATC (transcript of...
Air France – Airbus – A320-311 (G-GLZC) flight no. AF3682
Air France flight AF3682 was on ILS final approach to runway 08 at Cayenne-Rochambeau aerodrome, the airplane encountered windshear and sank suddenly at a height of a hundred feet. A "SINK RATE" warning sounded. The Co-pilot, at the controls, pulled back on the...
Aviation accidents
 An aviation accident is an incident in which an aircraft is damaged or destroyed as a result of a collision, fire, structural failure, or other event. Aviation accidents can be caused by a variety of factors, including mechanical failure, pilot error, adverse weather conditions, and sabotage. Aviation accidents can result in fatalities, injuries, and damage to property.
An aviation accident is an incident in which an aircraft is damaged or destroyed as a result of a collision, fire, structural failure, or other event. Aviation accidents can be caused by a variety of factors, including mechanical failure, pilot error, adverse weather conditions, and sabotage. Aviation accidents can result in fatalities, injuries, and damage to property.
Aviation incidents
 An aviation incident is an occurrence, other than an accident, that affects or could affect the safety of aircraft operations. Examples of aviation incidents include near collisions, runway incursions, and unruly passenger incidents.
An aviation incident is an occurrence, other than an accident, that affects or could affect the safety of aircraft operations. Examples of aviation incidents include near collisions, runway incursions, and unruly passenger incidents.
Aviation serious incidents

A serious incident in aviation refers to an event that could have resulted in an accident or that had the potential to cause serious injury or death. Some examples of serious incidents in aviation include engine failure, in-flight fires, and loss of control of the aircraft.